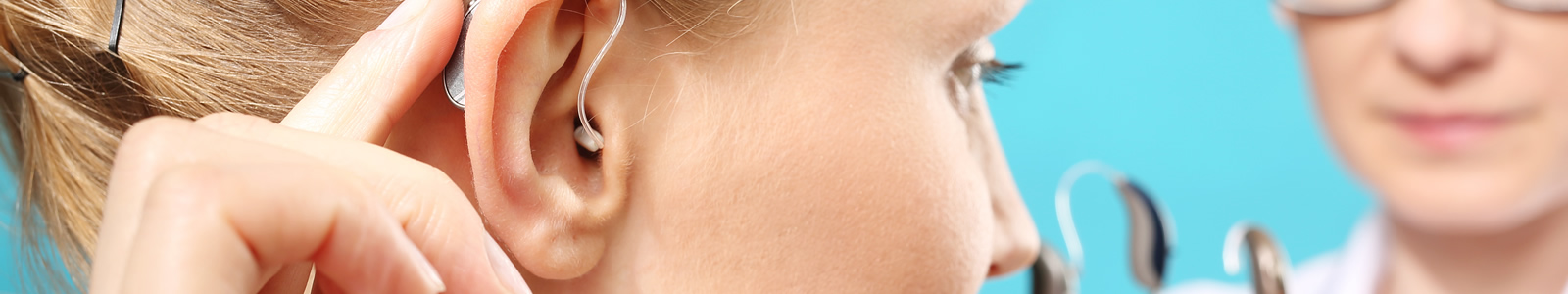
You may have hearing loss, and not even be aware of it. People of all ages experience gradual hearing loss, often due to the natural aging process or long exposure to loud noise. Other causes of hearing loss include viruses or bacteria, heart conditions or stroke, head injuries, tumors, and certain medications. Treatment for hearing loss will depend on your diagnosis.
The aural or hearing-sense is a complex and intricate process. The ear is made up of three sections: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. These parts work together so you can hear and process sounds. The outer ear, or pinna (the part you can see), picks up sound waves and the waves then travel through the outer ear canal.
When the sound waves hit the eardrum in the middle ear, the eardrum starts to vibrate. When the eardrum vibrates, it moves three tiny bones in your ear. These bones are called the hammer (or malleus), anvil (or incus), and stirrup (or stapes). They help sound move along on its journey into the inner ear.
The vibrations then travel to the cochlea, which is filled with liquid and lined with cells that have thousands of tiny hairs on their surfaces. The sound vibrations make the tiny hairs move. The hairs then change the sound vibrations into nerve signals, so your brain can interpret the sound.
Answer the following questions then calculate your score. To calculate your score, give yourself 3 points for every “Almost always” answer, 2 points for every “Half the time” answer, 1 point for every “Occasionally” answer, and 0 for every “Never.” Please note: If hearing loss runs in your family, add an additional 3 points to your overall score.
The American Academy of Otolaryngology—Head and Neck Surgery recommends the following:
0-5 points — Your hearing is fine. No action is required.
6-9 points — Suggest you see an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist.
10+ points — Strongly recommend you see an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist.
I have a problem hearing over the telephone
I have trouble following the conversation when two or more people are talking at the same time.
People complain that I turn the TV volume too high.
I have to strain to understand conversations.
I miss hearing some common sounds like the phone or doorbell ring.
I have trouble hearing conversations in a noisy background, such as a party.
I get confused about where sounds come from.
I misunderstand some words in a sentence and need to ask people to repeat themselves.
I especially have trouble understanding the speech of women and children.
I have worked in noisy environments (such as assembly lines, construction sites, or near jet engines).
Almost always
Many people I talk to seem to mumble, or don't speak clearly.
People get annoyed because I misunderstand what they say.
I misunderstand what others are saying and make inappropriate responses.
I avoid social activities because I cannot hear well and fear I'll make improper replies.
Ask a family member or friend to answer this question: Do you think this person has a hearing loss?